Knowledge of first aid is an important life skill that can save a life and prevent further injuries. A tourniquet temporarily stops the flow of blood, until proper medical attention is provided. Three techniques in applying a tourniquet include make-shift technique, surgical, and emergency technique.
[youtube url=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sjOStXVvsGU” width=”220″]Make-shift technique
The make-shift tourniquet is applied to minor pains such as in the hands, wrist, foot and ankle. This is done by securing the areas near the injured part of the body tightly with a string or tape in order to stop the bleeding. It should be tight to stop the arterial blood flow. The size of the tourniquet should be between 1 to 2 inches wide. If the tourniquet is narrow, it will cut into the skin when you apply pressure. If a wider tourniquet is used, more pressure is applied to stop the bleeding. When applying a tourniquet on the legs, it should be narrower than those on the arm, because it is due to the pressure applied to stop blood flow of blood in the legs.
The surgical technique
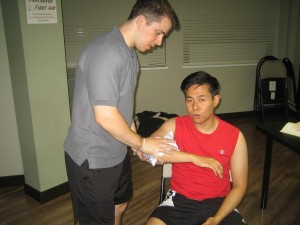
The surgical technique is applied when a person has lost substantial amount of blood. It involves stopping the bleeding to the injured part by applying an elastic bandage close to one end of the injury and another at the other end and then cover it with a sleeve or cloth. This will keep the injury stabilized and protected before a surgery can be performed.
The emergency technique
The emergency tourniquet is applied as a last resort by wrapping the injured area with gauze or cloth or anything available just to stop the bleeding. When stabilizing the injured part of the body, a piece of stick or a rod-like object is placed at the side of the injured part and secure in place with additional gauze. In times of emergencies, this technique is beneficial since it can stop the bleeding, however it can lead serious health problems. Emergency tourniquets completely stop the bleeding of the injured area but areas below the injured part cannot receive an adequate supply of blood and face the risk of amputation.
Possible health problems in applying the emergency tourniquet
1. Amputation – areas of the body that do not receive enough supply of blood
2. Palsy – a kind of paralysis where there is loss of feeling and shaking of the body
3. Pain – an unpleasant feeling caused by a damage on a body part such as stubbing a toe, cutting a finger and putting alcohol on a scrape
4. Clot – a thick or coagulated mass of blood that may cause heart attack, stroke, or other serious health problems
5. Acute renal failure – occurs when there is a condition that slows the flow of blood to your kidneys
6. Abscess – a pus that develops in response to infection
7. Blisters – small pockets of water on the upper layers of the skin caused by burning or exposure to chemicals
8. Abrasions – the skin is scraped from a hard surface
9. Contusions –caused by a blow from a round object
Tips to remember in applying tourniquets
• Careful placement of tourniquet near the site of bleeding must be observed at all time.
• Tourniquet time should only be less than 2 hours if possible.
• Minimize excessive application of pressure.
